2 Notation, Acronyms, and Conventions
Table 1Update* defines some acronyms used in this article. Since it is always clear from context, I use the same symbol for theoretical statistical quantities (e.g., underlying spectra) and estimates derived from finite data sets (e.g., sample spectra). All power spectra are two-sided.| Symbol |
Meaning |
| acf |
autocorrelation function |
| AMC |
Advanced Media Calibration system (see Section 4.3) |
| DOY |
day-of-year, i.e., January 20 = DOY 020 |
| DSN |
Deep Space Network, the NASA/JPL spacecraft communications and tracking network with antennas at complexes in Australia, Spain, and the United States |
| DSS |
Deep Space Station (identifier for specific antennas in the DSN, e.g., “DSS 25”) |
| f |
Fourier frequency |
| FTS |
Frequency and Timing System, the reference for two-way Doppler tracking |
| Ka-band |
a deep space communications frequency |
| KaT |
Cassini’s “Ka-band Translator” which accepts an uplink Ka-band signal and phase-coherently translates it to a downlink Ka-band signal for retransmission to earth |
| LISA |
Laser Interferometer Space Antenna, a future low-frequency GW observatory [24*] |
| one-way |
Doppler tracking where the downlink is referenced to an oscillator on the spacecraft |
| S-band |
a deep space communications frequency |
| scintillation |
phase fluctuation due to wave propagation in a random medium [106*, 79*, 40*, 99*, 71*] |
| SEP angle |
sun-earth-probe angle, the apparent solar elongation angle of the spacecraft |
| Sx(f) |
power spectrum of x(t), i.e., Fourier transform of |
| T |
duration of an observation |
| T2 |
two-way light time between earth and spacecraft |
| three-way |
Doppler tracking where the received downlink is coherently referenced to an uplink signal from another station |
| two-way |
Doppler tracking where the downlink is coherently referenced to the uplink signal |
| X-band |
a deep space communications frequency |
x  y y |
convolution of time series x(t) and y(t) [34] |
| y(t) |
generic time series of fractional frequency, |
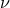 |
radio frequency |
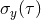 |
Allan deviation, fractional frequency stability at integration time
|
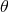 |
angle between GW propagation direction and earth-spacecraft vector;
|

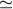 32 GHz
32 GHz
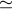 2.3 GHz
2.3 GHz 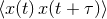
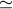 8.4 GHz
8.4 GHz 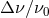
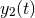 : time series of two-way Doppler fractional frequency)
: time series of two-way Doppler fractional frequency)
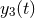 : time series of three-way Doppler fractional frequency)
: time series of three-way Doppler fractional frequency) 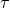
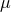 = cos(
= cos(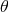 )
)