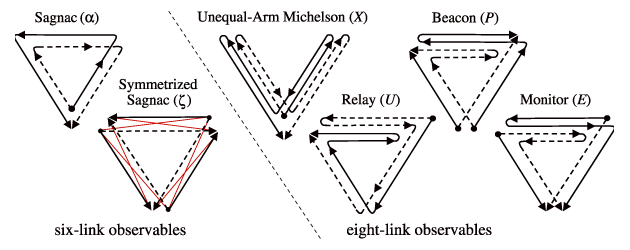
Figure 1: Time-Delay Interferometry (TDI). LISA-like detectors measure GWs by transmitting
laser light between three spacecraft in triangular configuration, and comparing the optical phase
of the incident lasers against reference lasers on each spacecraft. To avoid extreme requirements
on laser-frequency stability over the course of the many seconds required for transmission around
the triangle, data analysts will generate time-delayed linear combinations of the phase comparisons;
the combinations simulate nearly equal-delay optical paths around the sides of the triangle, and
(much like an equal-arm Michelson interferometer) they suppress laser frequency noise. Many such
combinations, including those depicted here, are possible, but altogether they comprise at most three
independent gravitational-wave observables. Image reproduced by permission from [447], copyright
by APS.

